
Effective Cricket Identification and Management for New York Homes and Businesses
New York City, with its bustling energy and towering skyscrapers, is a far cry from the serene countryside. Yet, amidst the urban jungle, a tiny, often overlooked creature thrives: the cricket. These chirping insects have adapted remarkably well to city life, making their presence known in homes, businesses, and other structures.
Understanding the nuances of cricket identification is crucial for effective pest management. While many people might dismiss them as harmless, certain cricket species can pose problems. They can damage property, contaminate food, and even trigger allergies.
New York’s diverse ecosystem supports a variety of cricket species. From the common house cricket, known for its incessant chirping, to the less familiar field cricket, these insects have found their niche in both urban and suburban environments. Identifying the specific type of cricket you’re dealing with will help determine the most appropriate control measures.
Cricket Identification
Crickets, while often dismissed as harmless, can become a nuisance and even cause damage in New York homes and businesses. Accurate identification is the first step to effective control.
Common Crickets in New York
Several cricket species commonly inhabit New York’s urban and suburban areas:

- House Crickets: These are the most common household invaders. They are typically brown or black, with a length of about 3/4 to 1 inch. House crickets are known for their constant chirping, often associated with warm, humid conditions.
- Field Crickets: Larger than house crickets, field crickets are often found outdoors but can enter homes in search of warmth. They are typically brown or gray and have a more robust appearance. While they can chirp, their song is less frequent than that of house crickets.
- Spider Crickets (Camel Crickets): These wingless crickets are often mistaken for spiders due to their long legs. They are typically light brown or gray and have a humped appearance. Unlike other crickets, spider crickets do not chirp.
- Cave Crickets: Similar in appearance to spider crickets, cave crickets prefer cool, damp environments. They are often found in basements and crawl spaces.
Visual Differences and Behaviors
To accurately identify cricket species, consider these visual cues and behavioral differences:
- Body shape: House crickets have a more slender body, while field crickets are more robust. Spider and cave crickets have a distinct humped appearance.
- Wing length: House and field crickets have wings, while spider and cave crickets do not.
- Color: House crickets are typically brown or black, while field crickets can vary from brown to gray. Spider and cave crickets are usually light brown or gray.
- Chirping: House crickets are known for their constant chirping. Field crickets chirp less frequently, and spider and cave crickets do not chirp at all.
- Habitat: House crickets prefer warm, dry environments, while field crickets are often found outdoors. Spider and cave crickets thrive in cool, damp conditions.
Cricket Life Span
While precise data on the lifespan of specific cricket species in New York might be limited, general information can provide valuable insights.
Average Lifespan of Common Cricket Types
- House Crickets: Typically, house crickets have a lifespan of about 3 months under ideal conditions. However, this can vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability.
- Field Crickets: Similar to house crickets, field crickets also have an average lifespan of around 3 months. However, their life cycle can be shorter due to exposure to outdoor elements and predators.
- Spider Crickets: While specific data on spider cricket lifespan is scarce, it’s generally believed that they live for a similar duration as house and field crickets.
- Cave Crickets: Like their counterparts, cave crickets are estimated to have a lifespan of around 3 months. However, their life cycle might be influenced by the specific conditions of their underground habitat.
Factors Affecting Cricket Life span
Several factors can influence the lifespan of crickets:

- Temperature: Warmer temperatures tend to accelerate a cricket’s metabolism, potentially shortening its lifespan.
- Humidity: Proper humidity levels are essential for cricket survival. Excessive dryness or humidity can negatively impact their lifespan.
- Food Availability: A consistent supply of food is crucial for crickets to thrive and reach their full lifespan potential.
- Predators: Outdoor crickets face a higher risk of predation, which can significantly reduce their lifespan.
- Indoor Conditions: Controlled indoor environments can extend a cricket’s lifespan compared to outdoor conditions.
Are Black Crickets Poisonous?
Black crickets are not poisonous to humans or pets. The color of a cricket does not determine its toxicity. In fact, many cricket species, including common house crickets, can be black or dark brown.
There are several common myths surrounding black crickets:
- Myth: Black crickets are more dangerous than other crickets.
- Fact: All cricket species are relatively harmless to humans and pets. The primary concerns with crickets are property damage, contamination of food, and allergic reactions.
- Myth: Black crickets carry diseases.
- Fact: While crickets can carry bacteria on their bodies, they are generally not known to transmit diseases to humans or pets. Proper hygiene practices, such as washing hands after handling crickets or areas where they have been present, are essential.
Do Crickets Carry Diseases?
While the risk is relatively low, crickets can indeed carry diseases.
They can be carriers of bacteria such as E. coli and salmonella. These bacteria can be transferred through their droppings or by direct contact with the cricket itself.
Health risks associated with crickets in homes:
- Contamination of food: Crickets can crawl on food preparation surfaces and contaminate food with bacteria.
- Allergies: Cricket droppings and shed exoskeletons can trigger allergic reactions in some people.
- Asthma: For individuals with asthma, exposure to cricket allergens can exacerbate symptoms.
- Psychological distress: A cricket infestation can cause stress and anxiety for homeowners.
Cricket Droppings
Cricket droppings are small, dark pellets, often resembling black pepper grains. They are typically found in areas where crickets congregate or hide, such as behind baseboards, in corners, or near food sources.
Recognizing cricket droppings is crucial for identifying an infestation. While seeing the actual crickets can be sporadic, finding their droppings is often a more reliable indicator of a problem. A significant amount of droppings suggests a larger infestation that requires immediate attention.
What Do Crickets Eat?
Crickets are omnivores, meaning they consume both plant and animal matter. Their diet can vary depending on their environment and the availability of food sources.
Typical Cricket Diet
Generally, crickets feed on:
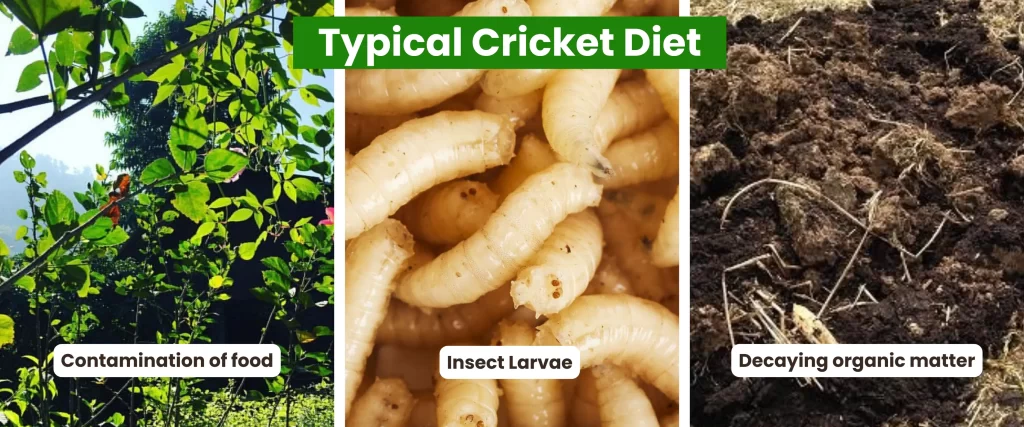
- Plant matter: This includes leaves, stems, flowers, fruits, and seeds.
- Insect larvae: Crickets are opportunistic feeders and will prey on smaller insects when available.
- Decaying organic matter: They also consume decomposing plant and animal matter.
Dietary Differences Among Cricket Species
While the general diet of crickets is similar, there can be some variations among different species. For example:
- House crickets: Often found indoors, these crickets may consume a wider variety of food items, including fabric, paper, and even human food scraps.
- Field crickets: As outdoor dwellers, field crickets typically have a diet richer in plant matter and insect prey.
- Spider crickets: These crickets are known to be more carnivorous, with a preference for insect prey.
What is the Difference Between a Cricket and a Grasshopper?

Often mistaken for each other, crickets and grasshoppers share some similarities but have distinct characteristics. To easily differentiate between a cricket and a grasshopper, focus on the following:
- Antennae length: Long antennae indicate a cricket, short antennae point to a grasshopper.
- Sound: Listen to how the insect produces its sound. Rubbing wings together suggests a cricket, while leg rubbing indicates a grasshopper.
- Time of day: If you see the insect during the day, it’s more likely a grasshopper. Nocturnal sightings lean towards a cricket.
How to Get Rid of Crickets?
Spider crickets, also known as cave crickets or camel crickets, can be a nuisance. Here’s how to control and eliminate them:
Control Methods

- Reduce moisture: Spider crickets thrive in damp environments. Use dehumidifiers in basements and crawl spaces to reduce humidity.
- Seal entry points: Inspect your home for cracks and crevices where spider crickets can enter. Seal these areas with caulk or weatherstripping.
- Vacuuming: Regularly vacuum areas where spider crickets are seen to remove adults and eggs.
- Sticky traps: Place sticky traps in areas where spider crickets are active to capture them.
- Diatomaceous earth: Sprinkle diatomaceous earth in areas where spider crickets are found. It will dehydrate and kill them.
- Professional pest control: For severe infestations, consider contacting a professional pest control service.
Prevention
- Proper ventilation: Ensure good ventilation in basements and crawl spaces to reduce humidity.
- Eliminate moisture sources: Fix leaky pipes and remove any standing water.
- Regular inspections: Check for signs of spider crickets regularly to detect infestations early.
- Screen windows and doors: Prevent spider crickets from entering your home by using screens.
Conclusion
Crickets, while often seen as harmless, can quickly become unwanted housemates. Understanding the different types of crickets prevalent in New York, their habits, and potential damage is crucial for effective management.
By carefully observing physical characteristics like body shape, wing length, and color, you can accurately identify the cricket species invading your space. This knowledge is essential for selecting the most appropriate control methods.
For severe infestations or persistent problems, consulting a professional pest control service is advisable. These experts have the knowledge and tools to effectively eliminate crickets from your home.



