What Types of Rodents Call New York Home?
New York City, a busy metropolis known for its varied population and iconic skyline, also shares its urban landscape with a variety of rodent species. These small, often nocturnal creatures can pose considerable challenges for residents, businesses, and public health officials.
Understanding the different types of rodents that call New York home is crucial for effective pest control and prevention. Accurate identification of rodent species is essential for several reasons:
- Tailored Pest Control: Different rodent species may demonstrate distinct rodent behaviors and preferences for habitats and food sources. Knowing the specific type of rodent infestation allows for targeted pest control measures.
- Disease Prevention: Some rodents, such as rats, can carry and transmit diseases like salmonella and hantavirus. Identifying the species involved helps in implementing proper disease prevention strategies.
- Property Damage: Rodents can cause major property damage by gnawing on wires, insulation, and structural materials. Understanding the type of rodent infestation can inform preventative measures to protect buildings and infrastructure.
Different Types of Rodents in New York
New York City is home to a various range of rodent species, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. The most common rodents found in the city include:
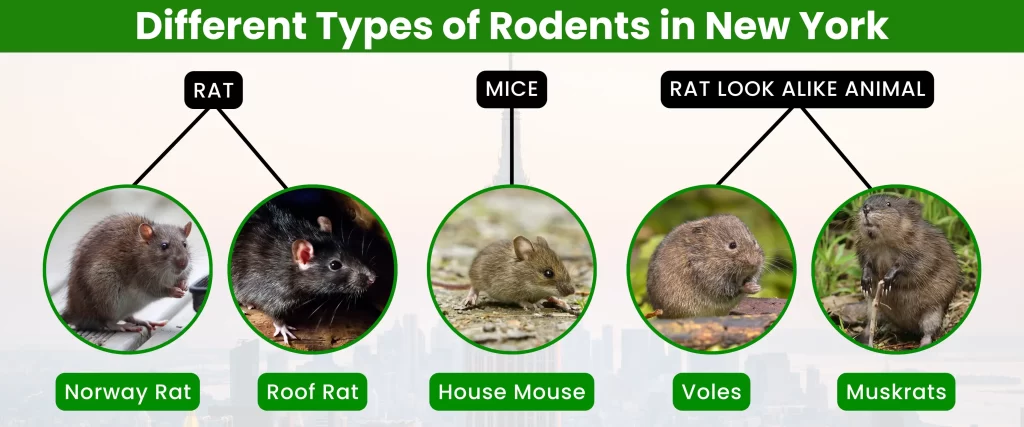
Rats
- Norway Rat (Rattus norvegicus): These large, brown rats are one of the most common rodent pests in urban areas. They are adaptable and can thrive in various environments, including sewers, basements, and garbage dumps.
- Roof Rat (Rattus rattus): Smaller and more agile than Norway rats, roof rats are often found in upper floors of buildings and trees. They are excellent climbers and can enter structures through small openings.
Mice
- House Mouse (Mus musculus): These tiny, gray mice are commonly found in homes, businesses, and other structures. They are highly adaptable and can reproduce rapidly, making infestations difficult to control.
Rat Look Alike Animal
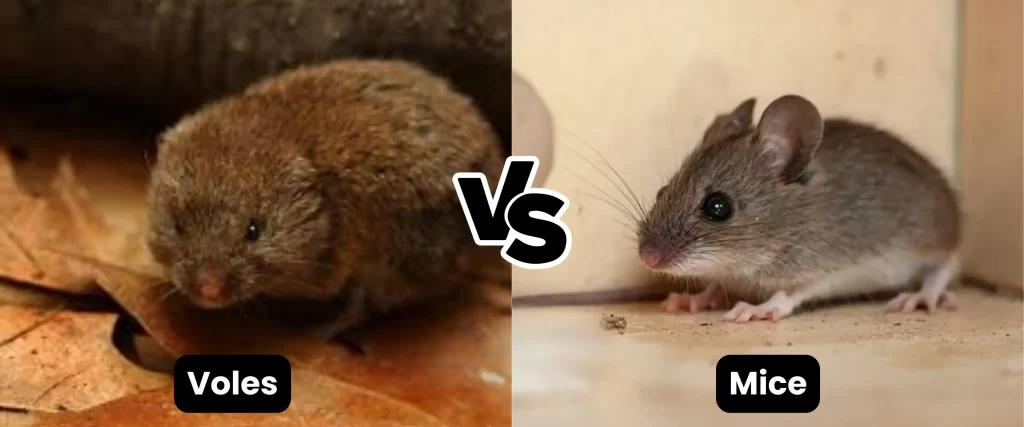
- Voles: These small rodents look like mice but have shorter tails and stouter bodies. They are often found in grassy areas and gardens, where they can cause damage to plants.
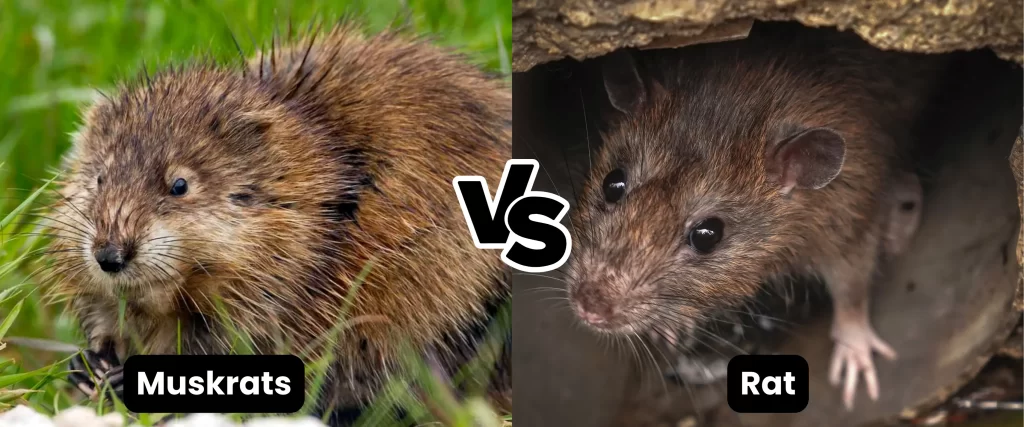
- Muskrats: These semi-aquatic rodents are larger than rats and have a musky odor. They are typically found near water bodies, such as ponds and streams.
Are Mice Dangerous?
Yes, mice are dangerous, while they may seem harmless but can pose significant health risks to humans. One of the primary concerns is their potential to spread diseases. Mice can contaminate food and water sources with bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Some of the diseases that mice can transmit include:

- Salmonella: A bacterial infection that can cause food poisoning, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps.
- Hantavirus: A viral infection that can cause respiratory illness, including fever, cough, and shortness of breath.
- Rat-bite fever: A bacterial infection caused by a bite from a rat or mouse. Symptoms include fever, headache, and muscle pain.
In addition to spreading diseases, mice can also cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Their fur, dander, and urine can contain allergens that can cause symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
Field Mice in House: Are They Dangerous?
Field mice, while typically found in outdoor environments, may occasionally enter into homes in search of food, water, or shelter. While they may not be as common as house mice, they can still pose a threat to residential areas.
Behavior When Entering Homes
When field mice enter homes, they often seek out warm, isolated places to nest. They may be found in attics, basements, or other areas that provide shelter and protection. Field mice are typically nocturnal and may be more active at night.
Specific Dangers
Field mice can pose similar health risks to house mice, including:
- Disease transmission: Field mice can carry and transmit diseases such as hantavirus and salmonella.
- Property damage: Field mice may gnaw on wires and insulation, potentially causing electrical problems or structural damage.
- Contamination: Their droppings and urine can contaminate food, surfaces, and insulation, leading to health risks and unpleasant odors.
Identifying and Differentiating Rodents
Accurate identification of rodent species is crucial for effective pest control. Here are some tips on how to distinguish between different types of rodents:
Appearance:
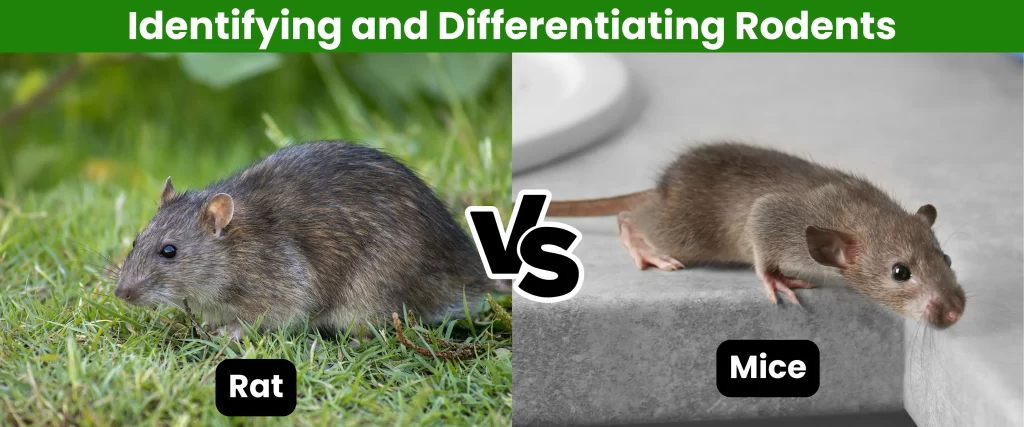
- Size: Rats are generally larger than mice, with longer bodies and tails.
- Color: The color of a rodent can provide clues about its species. For example, Norway rats are typically brown, while roof rats may have a darker coat with a white belly.
- Tail: The tail can be a helpful indicator. Rats have longer tails that are often hairless, while mice have shorter, furrier tails.
- Body shape: Rats tend to have a more robust build, while mice are typically more slender.
Behavior:
- Activity: Some rodents are more active during the day (diurnal), while others are primarily active at night (nocturnal).
- Habitat: The location where you see the rodent can provide clues about its species. For example, roof rats are often found in upper floors of buildings and trees, while Norway rats may be more common in basements and sewers.
- Sounds: Different rodents may produce distinct sounds, such as squeaking, scratching, or gnawing.
Visual and Behavioral Clues:
- Rats vs. Mice:

rat vs mice Rats are generally larger than mice and have longer tails. They may also be more likely to gnaw on wires and insulation. Mice are smaller and have shorter tails. They are often found in kitchens and pantries, where they can access food.
- Voles vs. Mice:

Voles vs mice Voles are similar in size to mice but have shorter tails and stouter bodies. They are often found in grassy areas and gardens.
- Muskrats vs. Rats:

muskrats vs rat Muskrats are larger than rats and have a distinctive musky odor. They are typically found near water bodies.
Preventing and Managing Rodent Infestations
Preventing Rodent Infestations

- Seal entry points: Inspect your home for any cracks or gaps in the foundation, walls, or roof. Seal these openings with caulk or steel wool to prevent rodents from entering.
- Eliminate food sources: Store food in airtight containers, especially grains, nuts, and pet food. Clean up crumbs and spills promptly.
- Remove clutter: Clutter can provide hiding places for rodents. Keep your home and yard free of debris and clutter.
- Regular inspections: Conduct regular inspections of your home, both inside and out, to identify potential rodent entry points or signs of infestation.
- Garbage management: Store garbage in sealed containers and place them away from your home. Avoid leaving food scraps outside.
Steps to Take If You Suspect a Rodent Problem
- Inspect for signs: Look for signs of rodent activity, such as droppings, gnawed wires, or tracks.
- Seal entry points: If you find evidence of rodents, seal any entry points they may be using.
- Set traps: Place humane traps near areas where you have seen evidence of rodents. Be sure to bait the traps with food or peanut butter.
- Consider professional help: If the infestation is severe or you are unable to control it on your own, it may be necessary to seek professional pest control services.
When to Seek Professional Help

- Large-scale infestations: If you have a large-scale rodent infestation, it may be difficult to control it on your own. Professional pest control services have the experience and tools to handle such problems.
- Health concerns: If you are concerned about the potential health risks associated with rodents, such as the spread of diseases, it is advisable to consult with a professional pest control company.
- Recurring infestations: If you have recurring rodent problems, professional pest control services can help identify the underlying causes and implement effective prevention measures.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of rodents that call New York home is essential for effective pest control and prevention. By identifying the species involved, you can tailor your approach to address specific behaviors and habitats. This knowledge can help you prevent infestations, protect your property, and safeguard your health.
Keeping your home rodent-free requires vigilance and proactive measures. Regularly inspect your property for signs of rodent activity, seal entry points, eliminate potential food sources, and maintain a clean environment. If you suspect a rodent infestation, don’t delay in taking action. Early detection and intervention can help prevent further damage and reduce the risk of health problems.
Remember, a rodent infestation is a serious matter that should not be ignored. By taking the necessary steps to prevent and manage these pests, you can protect your home, your family, and the community at large.






