
Pigeons have long been a familiar sight in urban environments, including New York City. They are often perceived as harmless, even endearing, creatures. Their constant presence has made them almost a symbol of the city for many. However, this benign image masks a more complex reality.
Types of Pigeons in NY and their Behavior
While the term “pigeon” is often used generically, there are actually several species and subspecies found in New York City. The most common is the Rock Dove, which is the ancestor of domesticated pigeons. These birds have adapted remarkably well to urban life, thriving in the city’s unique ecosystem.
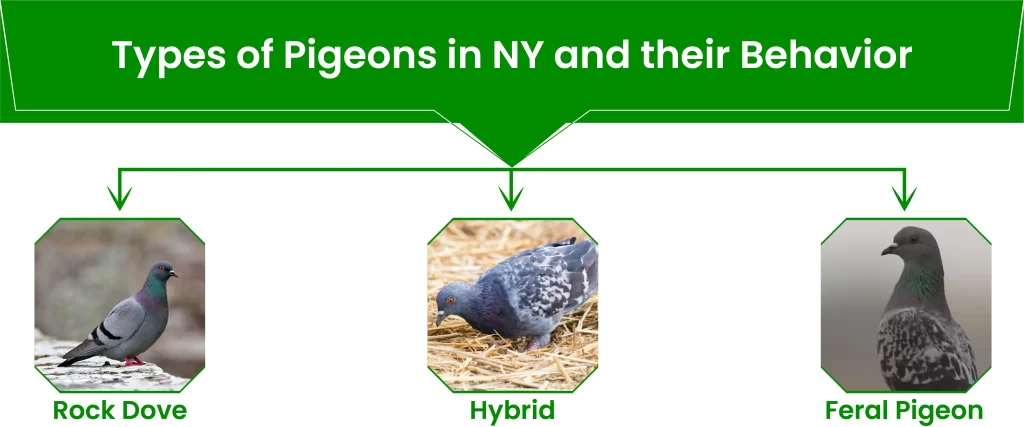
- Rock Dove: The quintessential city pigeon, characterized by its grey and white plumage. They are highly adaptable and can be found in every borough.
- Feral Pigeon: A domesticated pigeon that has reverted to a wild state. They often exhibit a mix of domestic and wild behaviors.
- Hybrids: Crossbreeds between Rock Doves and domesticated pigeons, displaying a variety of colors and patterns.
Pigeons of new york are Problematic
While pigeons might seem innocent, their behavior can cause significant issues for city dwellers and infrastructure.The behavior of the pigeons, particularly their ability to thrive in urban settings, contributes to their problematic nature. They are highly adaptable, finding food and shelter with ease. Their rapid reproduction rate allows them to maintain large populations. Additionally, their fearless nature and tendency to flock can lead to aggressive behavior and property damage.
- Disease Transmission: Pigeons can carry and transmit diseases such as histoplasmosis, salmonellosis, and cryptococcosis. Their droppings can contaminate food sources and public areas.
- Property Damage: Pigeon droppings are acidic and can damage buildings, statues, and vehicles. Nesting materials can clog gutters and air conditioning units.
- Public Health Concerns: Large pigeon populations can create unsanitary conditions and attract other pests. Their droppings can also trigger allergies and respiratory problems in humans.
- Noise Pollution: Large flocks of pigeons can produce excessive noise, disturbing residents and businesses.
- Agricultural Damage: In some cases, pigeons can cause damage to crops and compete with other bird species for resources.
The Problems Caused by New York Pigeons
Health Risks Associated with Pigeon Presence

While pigeons might seem harmless, they pose significant health risks to city dwellers.
- Disease Transmission: Pigeons can carry and transmit various diseases, including:
- Histoplasmosis: A lung infection caused by inhaling spores from pigeon droppings.
- Cryptococcosis: A fungal infection that can affect the lungs, brain, and other organs.
- Salmonellosis: A bacterial infection causing diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps.
- Psittacosis: A respiratory disease caused by a bacteria found in pigeon droppings.
- Allergies and Respiratory Issues: Pigeon droppings can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory problems, especially in individuals with asthma or other sensitivities.
Damage to Property and Infrastructure
Pigeon infestations can cause substantial damage to both residential and commercial properties.

- Building Damage: Pigeon droppings are acidic and can erode building facades, statues, and monuments. Nesting materials can clog gutters and drains, leading to water damage.
- Vehicle Damage: Pigeon droppings can damage car paint and windshields, making them unsightly and reducing the vehicle’s value.
- Public Health and Safety: Accumulated droppings create slippery conditions, increasing the risk of falls and accidents.
How Pigeons Adapt to Urban Environments
Pigeons have demonstrated remarkable adaptability to urban living, allowing them to thrive in the concrete jungle.
- Food Availability: Human activities provide a consistent food source for pigeons. Leftovers, crumbs, and discarded food attract them to parks, sidewalks, and garbage areas.
- Shelter and Nesting Sites: Buildings offer ample shelter and nesting opportunities. Rooftops, ledges, and crevices provide safe havens for pigeons to roost and raise young.
- Lack of Natural Predators: The absence of natural predators in urban environments allows pigeon populations to grow unchecked.
Reasons for Their Large Population Despite Urban Challenges
Despite the challenges of city life, pigeon populations continue to flourish.
- High Reproductive Rate: Pigeons have a high reproductive rate, producing multiple broods per year. This rapid reproduction contributes to population growth.
- Human Feeding: The practice of feeding pigeons encourages their presence and leads to increased population densities.
- Lack of Effective Control Measures: Challenges in implementing and enforcing pigeon control measures contribute to their persistence.
Environmental Impact and Concerns
Impact on Local Ecosystems and Other Bird Species
While pigeons have adapted remarkably to urban environments, their presence can negatively impact local ecosystems and other bird species.
- Competition for Resources: Pigeons compete with native bird species for food and nesting sites, potentially displacing them from their preferred habitats.
- Disease Transmission: Pigeons can carry diseases that may be transmitted to other bird species, impacting their populations.
- Ecological Imbalance: Large pigeon populations can disrupt the delicate balance of urban ecosystems, leading to unforeseen consequences for other wildlife and plant life.
Contribution to Urban Pollution and Sanitation Issues

Pigeon droppings contribute significantly to urban pollution and sanitation problems.
- Air Quality: Droppings release ammonia and other pollutants into the air, contributing to respiratory issues and air quality degradation.
- Water Contamination: Runoff from contaminated areas can carry harmful bacteria and pathogens into waterways, posing risks to aquatic life and human health.
- Aesthetic Impact: Pigeon droppings and nests can deface buildings, monuments, and public spaces, diminishing the city’s visual appeal.
Ethical Considerations: Removing Pigeons Humanely
The increasing awareness of animal welfare has led to a growing demand for humane and ethical pest control methods. When dealing with pigeons, it’s essential to prioritize solutions that minimize harm to the birds while effectively addressing the problems they cause.
How to Get Rid of Pigeons Naturally

Numerous humane methods can be employed to discourage pigeons from inhabiting specific areas.
- Physical Barriers:
- Bird netting: Creating a physical barrier to prevent pigeons from accessing roosting or nesting sites.
- Bird spikes: Deterrents that make landing surfaces uncomfortable for pigeons.
- Wire mesh: Used to cover vents and openings to prevent entry.
- Visual Deterrents:
- Scarecrows and decoys: Mimicking predators or other threats to scare pigeons away.
- Reflective objects: Using shiny materials to create a disorienting effect.
- Laser deterrents: Employing laser beams to disrupt pigeon behavior.
- Auditory Deterrents:
- Ultrasonic devices: Emitting high-frequency sounds that are unpleasant to pigeons but inaudible to humans.
- Distress calls: Playing recordings of predator calls or pigeon distress calls to frighten pigeons away.
Importance of Ethical Pest Control Practices
Ethical pest control involves several key principles:
- Humane treatment: Avoiding methods that cause pain, suffering, or death to animals.
- Environmental responsibility: Minimizing the impact on the environment and non-target species.
- Public health and safety: Protecting human health and preventing the spread of diseases.
- Long-term solutions: Focusing on sustainable and effective approaches to manage pigeon populations.
Natural and Effective Pigeon Deterrents
Many natural methods can be used to deter pigeons without resorting to harmful chemicals or traps.
- Plant repellents: Certain plants, such as lavender, mint, and chili peppers, have strong odors that pigeons dislike.
- Predatory bird silhouettes: Placing cutouts of predatory birds can create a visual deterrent.
- Water sprays: Using motion-activated sprinklers to startle pigeons.
- Habitat modification: Removing food sources and eliminating attractive nesting sites.
- Exclusion methods: Preventing access to buildings and other desirable areas.
Practical Tips for Pigeon Control in Urban Areas
Steps Individuals Can Take to Minimize Pigeon Presence
While city-wide and building-level strategies are crucial, individuals can also contribute to pigeon control efforts.
- Avoid feeding pigeons: This directly reduces their food supply and discourages their presence.
- Properly dispose of food scraps: Securely cover garbage cans and avoid leaving food remnants outdoors.
- Clean up after pets: Remove pet food and water bowls when not in use.
- Report pigeon infestations: Inform local authorities or building management about significant pigeon problems.
Advice for Building Managers and City Officials
Building managers and city officials play a pivotal role in pigeon control.
- Regular cleaning: Remove pigeon droppings and nesting materials promptly to discourage reoccupation.
- Implement deterrents: Install physical barriers, visual deterrents, or auditory repellents as needed.
- Collaborate with neighbors: Coordinate efforts with neighboring buildings to maximize the impact of control measures.
- Educate residents: Inform tenants and the public about the importance of responsible feeding and the impact of pigeons.
- Consider professional Pest Control Service: For severe infestations, consult with pest control experts specializing in bird management.
Conclusion
New York City’s pigeon population presents a complex challenge with far-reaching consequences. From public health risks to property damage and environmental impacts, the problems associated with pigeons are substantial. However, by understanding the factors contributing to their proliferation and implementing humane and effective control measures, it’s possible to mitigate these issues and create a more harmonious urban environment.



